Introduction
Clinical research is inherently complex, involving multiple stakeholders, regulatory hurdles, and significant financial investments. The success of these research initiatives hinges not only on scientific expertise but also on effective project management. Project Management Professionals (PMPs) bring structured frameworks and methodologies that can optimize resource allocation, streamline processes, and enhance overall project outcomes.
By applying the principles outlined in the Project Management Institute’s PMBOK® Guide, PMPs can address common challenges in clinical trials—such as delays, budget overruns, and compliance issues—ensuring that projects remain on schedule and deliver meaningful results. This article explores how PMPs can drive efficiency in clinical research through meticulous planning, risk management, and quality control.
Time Management and Resource Allocation: Optimizing Project Timelines
One of the most significant challenges in clinical research is adhering to strict timelines. Delays can lead to increased costs, lost funding opportunities, and setbacks in bringing life-saving therapies to market. PMPs are trained to develop realistic schedules and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that project milestones are achieved on time.
Key strategies for time management include:

Effective time management reduces the likelihood of delays and ensures that all project phases—from site initiation to final data analysis—proceed smoothly.
Risk Management: Anticipating and Mitigating Issues
Risk management is a cornerstone of project success, especially in clinical research where regulatory compliance, patient safety, and data integrity are paramount. PMPs employ structured risk management frameworks to identify potential issues early and develop mitigation strategies.
Steps in clinical research risk management include:
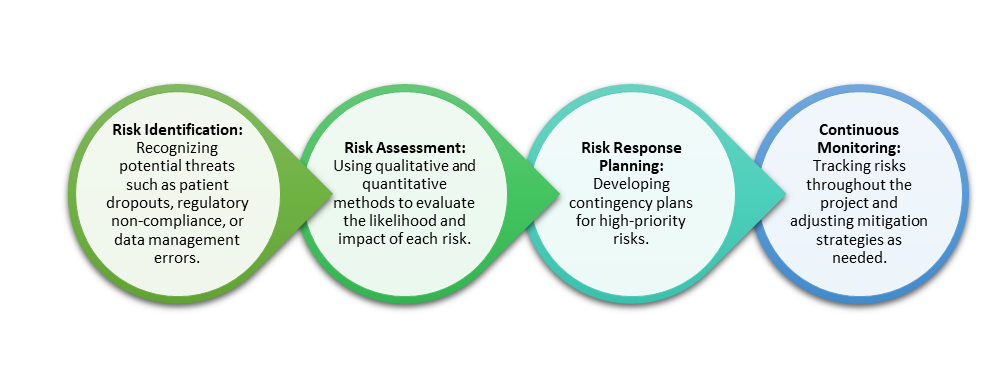
Proactive risk management not only minimizes disruptions but also enhances the credibility and reliability of research outcomes.
Quality Control and Compliance: Upholding Regulatory Standards
Maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements, such as Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) standards, is essential in clinical research. PMPs play a critical role in ensuring that every aspect of the trial adheres to these regulations.
Key aspects of quality control include:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Developing clear SOPs to ensure consistency across all research sites.
- Quality Assurance Audits: Conducting regular audits to identify discrepancies and implement corrective actions.
- Data Monitoring Committees (DMCs): Establishing independent committees to monitor data integrity and patient safety during the trial.
By integrating quality control measures into every project phase, PMPs help maintain regulatory compliance, reduce the risk of costly errors, and uphold the integrity of research findings.
Enhancing Team Collaboration: Breaking Down Silos
Clinical research involves diverse teams, including scientists, clinicians, regulatory specialists, and data analysts. Miscommunication or siloed work can lead to project delays and inefficiencies. PMPs foster collaboration by:
- Establishing Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Ensuring that all team members understand their roles within the project framework.
- Facilitating Cross-functional Communication: Regular meetings and collaborative platforms encourage the sharing of ideas and updates.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing disputes promptly through mediation and negotiation techniques.
Strong team collaboration enhances productivity, ensures consistent progress, and promotes a unified approach toward achieving project goals.
Cost Management: Balancing Budgets and Deliverables
Clinical trials are resource-intensive, with costs often running into millions of dollars. PMPs apply cost management principles to control budgets without compromising quality.
Key cost management strategies include:

Efficient cost management not only keeps projects financially viable but also ensures that resources are allocated where they are most needed.
Leveraging Technology for Efficiency Gains
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency in clinical research. PMPs can implement digital tools to automate routine tasks, streamline data management, and improve communication.
Technological innovations include:
- Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems: Simplifying data collection and reducing manual errors.
- Project Management Software: Facilitating task scheduling, resource allocation, and real-time progress tracking.
- Remote Monitoring Tools: Enabling virtual site visits and reducing the need for travel, thereby cutting costs and saving time.
The integration of technology into project management processes accelerates timelines and improves overall research efficiency.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of PMPs in Clinical Research
As clinical research becomes increasingly complex, the need for structured project management has never been greater. PMPs offer a strategic advantage by optimizing resource allocation, managing risks, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
The application of project management principles leads to:
- Improved adherence to project timelines.
- Enhanced regulatory and ethical compliance.
- Streamlined resource utilization.
- Reduced costs without compromising research quality.
By embedding PMBOK®-based frameworks into clinical research operations, PMPs can transform project outcomes, paving the way for faster, more efficient delivery of innovative therapies.
